Integrating Concentrated Solar Power and Photovoltaics for Enhanced Energy Generation
Imagine tapping into the sun’s immense energy not with just a singular approach, but by marrying two synergistic technologies. Hybrid solar power plants stand at this intersection, seamlessly merging the strengths of concentrated solar power (CSP) and photovoltaic (PV) systems to maximize electricity production.
This innovative combination is like having a renewable energy power team working together to deliver clean and sustainable energy. With an observable uptrend in corporate funding dedicated to solar power, the confidence in the future of these hybrid installations is clear.
Whether you’re a novice intrigued by the scope of hybrid solar or an industry stakeholder weighing options, this guide will uncover the advantages, integration techniques, and boundless potential of this dual technology.
Understanding concentrated solar power and photovoltaics
Hybrid solar power plants integrate two distinct technologies: concentrated solar power and photovoltaics.
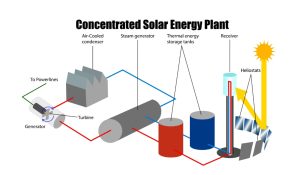
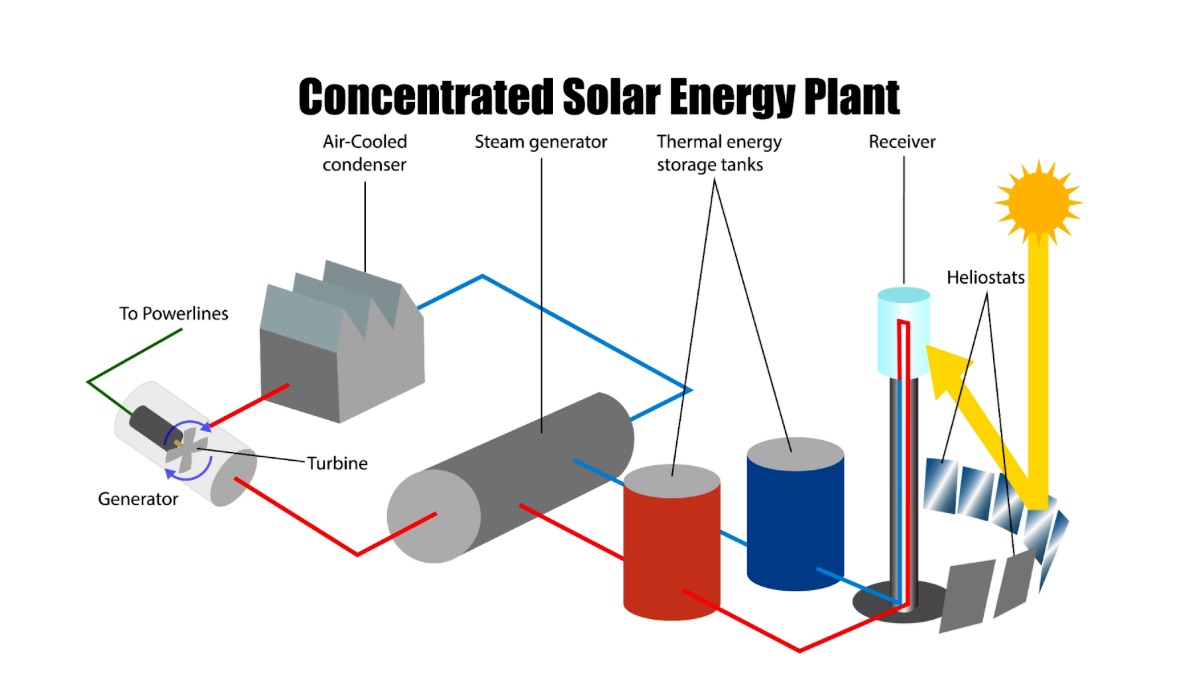
Concentrated solar power technology utilizes mirrors or lenses to direct sunlight onto a dedicated receiver. The concentrated light heats a fluid (often water or molten salt), which powers a turbine to generate electricity. The hallmark of CSP is its ability to store thermal energy, allowing for electricity generation even when the sun isn’t shining. This dispatchable power ensures grid stability, making it suitable for large-scale electricity generation and grid integration.
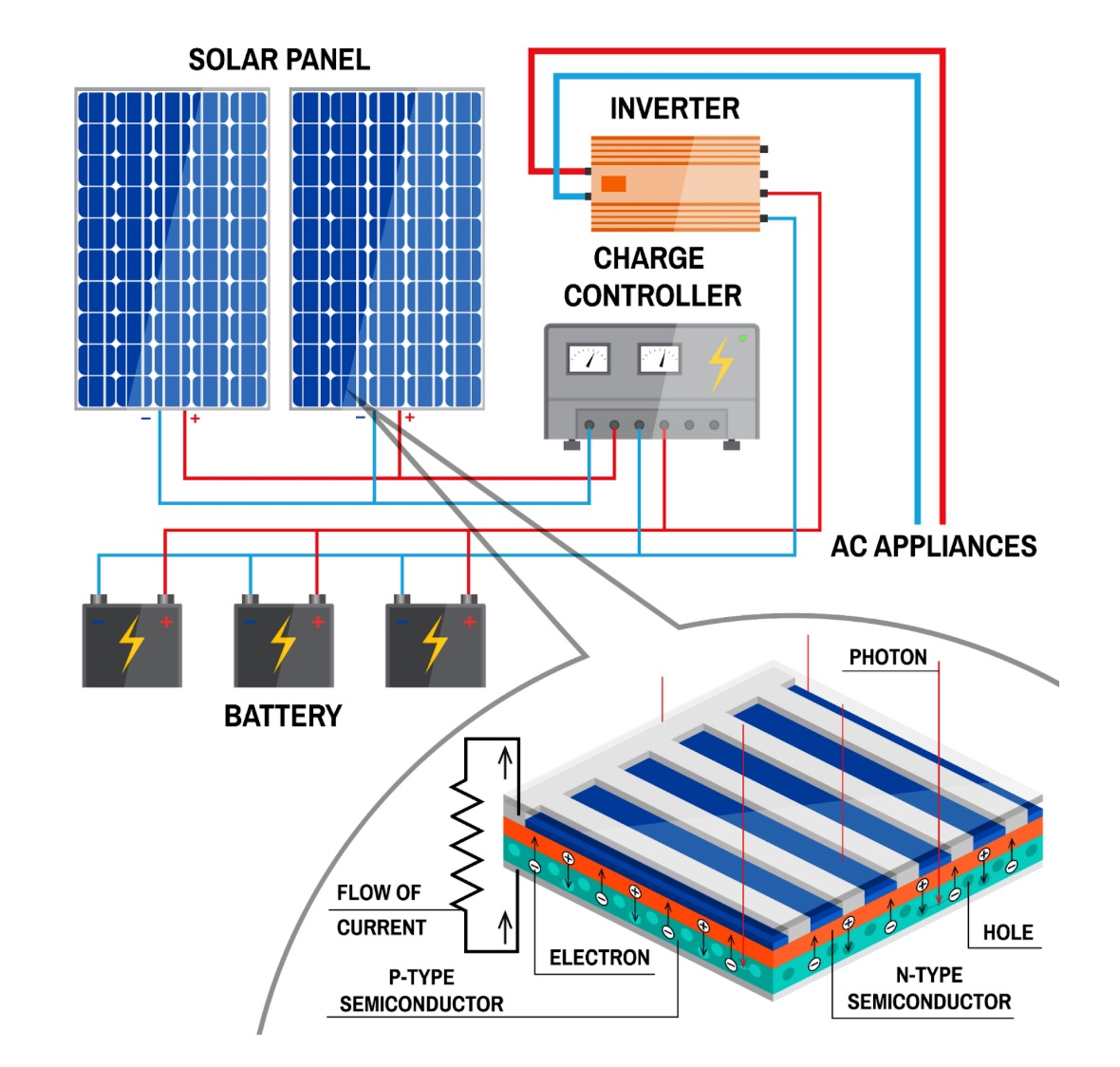
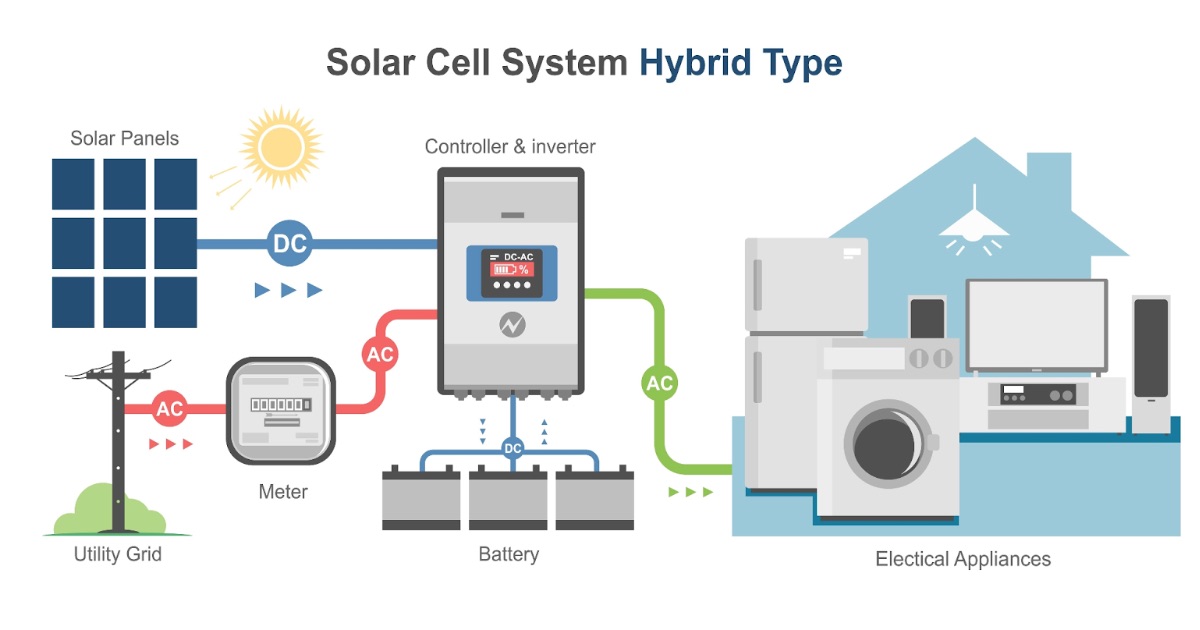
Photovoltaic technology converts sunlight into electricity using semiconductor materials. The sunlight excites the electrons inside the PV cells, producing an electric current. Due to its flexibility and scalability, PV technology can be tailored to various applications, ranging from small rooftop installations to sprawling solar farms.
While these systems are more reliant on sunlight, advancements in energy storage and photovoltaic efficiency are gradually negating this limitation. This is making PV an increasingly competitive option.
Synergy of CSP and PV in hybrid solar power plants
Combining CSP and PV in hybrid solar power plants is an evolutionary stride in maximizing energy generation. The integration of CSP’s thermal energy storage and PV’s direct electricity production equips these hybrid systems with more reliable and continuous power output.
Here are the key benefits of this CSP and PV fusion:
Balanced power generation
CSP’s higher capacity allows for sustained electricity generation, even under sub-optimal sunlight conditions. Conversely, PV systems peak during sunlit periods. Combining the two technologies allows hybrid solar power plants to achieve a more balanced and continuous power output, maximizing energy generation throughout the day.
Optimized land utilization
While CSP demands expansive land areas for sunlight concentration, PV systems can fit into compact spaces. Hybrid solar power plants can use CSP in open spaces and PV in areas with limited available and unconventional land, maximizing the overall energy production potential of the site.
Enhanced energy storage and flexibility
CSP systems can store excess heat and generate electricity during periods of low solar radiation, while PV systems produce electricity during peak sunlight hours. Surplus electricity from PV can also be used to charge thermal storage in CSP systems. This allows hybrid solar power plants to balance and manage energy more effectively.
Grid integration and system stability
By offering stable, dispatchable power, CSP supports grid stability even during fluctuations in demand. With their instantaneous power output, PV systems can help meet peak demand and reduce strain on the grid.
Eco-friendly energy source
Hybrid solar power plants drastically reduce greenhouse gas emissions, diminishing fossil fuel dependencies and fostering environmental conservation.
Integration modalities of CSP and PV
There are several ways of combining CSP and PV technologies. Each approach offers unique advantages for energy generation, system efficiency, and grid integration.
Co-located hybrid systems
Co-located systems involve installing CSP and PV units in the same location or adjacent land within a solar power plant. Each system operates independently while collectively enhancing overall energy yields.
Hybrid collector systems
This approach integrates CSP and PV functionalities within a single solar collector, capturing solar thermal energy and directly converting sunlight into electricity.
Integrated energy storage
Merging energy storage mechanisms ensures consistent and efficient power output. CSPs store excess thermal energy for later use, while PVs can charge the thermal energy storage.
The future outlook for hybrid solar power
Hybrid solar power plants represent a groundbreaking convergence of two powerful solar technologies: CSP and PV. Together, they effectively and efficiently harness the sun’s energy, achieving continuous electricity production by balancing each other’s strengths and limitations.
Recent renewable energy statistics estimate a nearly $1 trillion increase in the global renewable energy market by 2030. With an observable rise in investments, it’s evident that industry leaders and stakeholders recognize the unmatched potential of renewable energy solutions.
In fact, the Biden-Harris administration invested $45 million into manufacturing domestic solar components, creating a new market for American solar products. Given this momentum, along with the eco-friendly benefits, flexibility, and grid integration capabilities of hybrid solar systems, the future outlook is exceptionally bright.
As advancements continue to unfold, hybrid solar power plants will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping a sustainable and clean energy future for the world.
Zach Norton is a passionate advocate for sustainable energy solutions and awareness. With a deep commitment to combating climate change and promoting a greener future, Zach has dedicated his career to advancing the understanding of clean energy technologies and strategies.
Author: Zach Norton